Periodontics in McDonough, GA
Smile Creators Dentists Henry County, GA
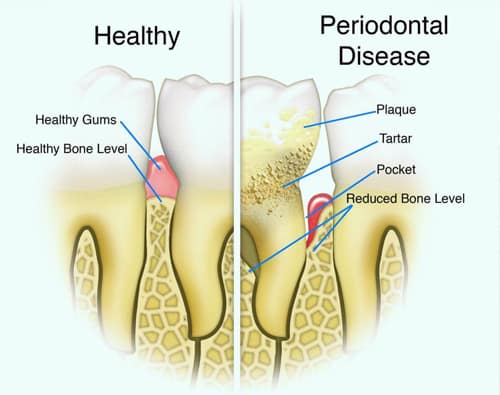
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an inflammatory disease that affects the tissues that surround and support your teeth. 47.2% of adults aged 30 years and older have some form of periodontal disease. Periodontal disease increases with age; 70.1% of adults 65 years and older have periodontal disease.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Bacteria in plaque, which is a sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on your teeth, causes gum disease. If plaque is not removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden and turn into tartar. Tartar can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist.
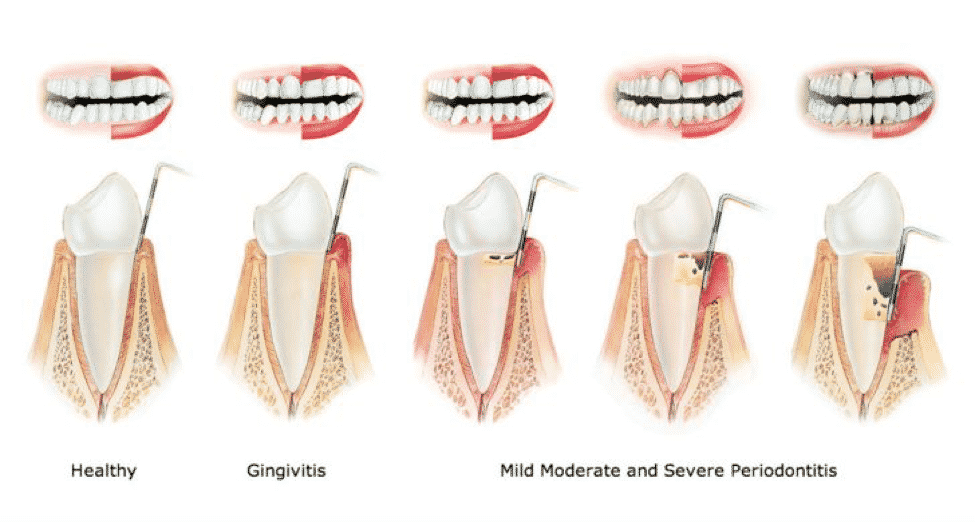
There are Three Stages of Gum Disease:
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup at the gum line. If daily brushing and flossing do not remove the plaque, it produces toxins (poisons) that can irritate the gum tissue, causing gingivitis. You may notice some bleeding during brushing and flossing. At this early stage in gum disease, damage can be reversed since the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place are not yet affected.
- Mild/Moderate Periodontitis: When gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a chronic infection that affects the gums and the bones that support the teeth. Bacteria and the body’s own immune system break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. Teeth may eventually become loose, fall out, or have to be removed.
- Severe Periodontitis: In this final stage of gum disease, the fibers and bone supporting your teeth are destroyed, which can cause your teeth to shift or loosen. This can affect your bite and, if aggressive treatment can’t save them, teeth may need to be removed.
How do I Know if I Have Gum Disease?
Gum disease can occur at any age, but it is most common among adults. If detected in its early stages, gum disease can be reversed so see your dentist if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Gums that are red, puffy or swollen, or tender
- Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing
- Teeth that look longer because your gums have receded
- Constant bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
- Gums that have separated, or pulled away, from your teeth, creating a pocket
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Pus coming from between your teeth and gums
How is Gum Disease Treated?
In order to properly diagnose the current condition of your mouth, an initial Comprehensive Oral Evaluation/Exam is done by the doctor. This exam is completed in addition with dental x-rays and periodontal probing (used to measure pocket depths around a tooth). Once your oral health has been accessed, we will discuss the best treatment method for you. The method of treatment will be determined by the type and severity of the disease.
The early stages of gum disease can often be reversed with proper brushing and flossing. Good oral hygiene will help keep plaque from building up.
The first nonsurgical step in treating periodontal disease usually involves a periodontal cleaning, called “scaling and root planing”. This is sometimes referred to as a “deep cleaning”. The initial treatment is done to remove plaque and tartar deposits on the tooth and root surfaces. This procedure helps gum tissue to heal and periodontal pockets to shrink.
Once your deep cleaning has been completed, the next step is your Periodontal Maintenance. This cleaning is recommended every 3-4 months in order to “maintain” your oral health. It is the most conservative approach to prevent more extensive and aggressive treatment—such as surgical therapy which may include flap surgery and bone and tissue grafts.

